One cannot have too large a party. A large party secures its own amusement.
~ Jane Austen, Emma (1816)
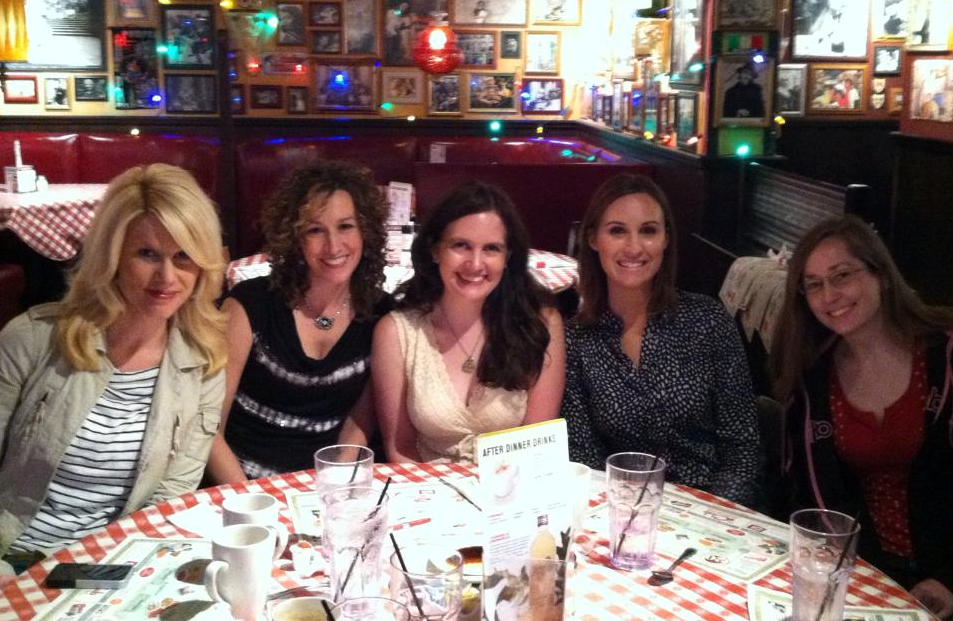
I’m sitting in an Italian restaurant in downtown Indianapolis on a perfect Sunday afternoon, with my hands wrapped around the warm mug of an after-dinner cappuccino. As I look around the table at my friends (authors with whom I share a particular passion for reading and writing Christian fiction), I see familiar smiles. There’s laughter. Good food being passed around family-style. Talk of husbands and children. We engage in chat about the publishing industry and brainstorm storyline this and character that… And although none of us had to drive all that far to reach our small Sunday feast, this quiet afternoon in June became something of an unexpected getaway.
It made a holiday out of the everyday.
Our topic of focus this month is vacationing. And while many of us immediately think of vacationing as going away on a retreat (perhaps to the seashore or to an English cottage in the countryside), there are many definitions of a holiday that can remain quite close to home. Though the outdoor balls, picnicking and formal parties of the Regency defined the summer holidays in many ways, we may find that our modern celebrations are not all that different…
So in homage to the feast, festival, backyard barbecue and the good old county fair, here’s a little fun for finding a holiday in the commonplace, everyday gathering – the party!
To Fête or Not to Fête
n. a feast or festival, a celebration, party; v. to celebrate or throw a party
The first use of the term fête is debatable. My mighty authors’ Thesaurus Rex App cites its first use in England by art historian and writer Horace Walpole (1717-97), followed by the first use of verb form in 1819. However, numerous historical resources cite the term to have been widely used in 17th Century Europe, as in the famous The Village Fête painting by Flemish painter Peter Paul Rubens (1635) Village Fête by French painter Claude Lorrain (1639), and in the 18th Century, to describe painter Jean Antoine Watteau’s work as fête galante (a French term used to describe the lofty yet idle recreation of the aristocracy under the reign of Louis the XIV).
The English term fête comes from the French for the same word, and could also refer to the formal party or social gathering that was frequented in the Regency.
“Formal visits, balls and other social occasions feature largely in Jane Austen’s letters… those who could afford it, and who had time and the space, gave parties. Such social gatherings were the recognized means of meeting people…”
Dominique Enright, The Wicked Wit of Jane Austen
In Great Britain, the fête was a village fair, or carnival of sorts, that would include any number of amusements. They showcased games, outdoor activities, crafts, livestock and produce, and homemade baked goods and canning. (This would be comparable to the modern street fair or country festival in the States.) Though not all specific to the Regency alone, an interesting list of village fête attractions included raffles, coconut shies (late 1800s), bat-a-rat, tug of war, fashion shows, and music and dancing.
One Mighty Famous Fête
As parties were frequently held by the Regency Era’s elite, there are several notable events that stand out through history. One such famous party was the Prince Regent’s Fete, held on June 19, 1811 at Charlton House. This was a marvelously sumptuous party thrown to celebrate the King’s birthday (though history argues that the true reasoning was to celebrate the lavishness of the Prince’s Regency). Invitations went out, though not everyone made an appearance. The Queen and her daughters (including Princess Charlotte) would not attend out of protest for such a party being held while the king was taken with illness.
[Wish to read more? Click HERE. Wondering what the impacts were for the Prince Regent after the famous event? Click HERE.]
Another famous fête occurred at the Tower of London in 1840. It’s a bit after the Regency Era, but still worth noting because of the guest list: a young Charles Dickens, artist George Cruikshank and host, novelist William Harrison Ainsworth. [Wish to read more? Click HERE.]

Fêtes in Fiction
The ball, formal party, or fête, is a common setting for many Regency romances – just as are the notable guests that may make an appearance at them. I happen to adore Jane Austen’s ball at Netherfield Park, as a major setting in the iconic Pride and Prejudice. That may be the one that gets the most press, but there are so many others! So while I finish off the last of my sweet Italian cappuccino and say a final fare-thee-well to my dear author friends, we’d like to hear from you, our readers. You’re here because you adore the Regency. So tell us –
What’s your favorite Regency fête in fiction, and why?
Share your favorite fête scenes with us here – we look forward to adding them to our recommended reading list with those deliciously lavish parties as setting number one!
[And for a little extra fun, here’s a link to the Regency Ball at Bath, 2010. Click HERE.]
In His Love,
Kristy
Originally posted 2013-06-10 10:00:35.

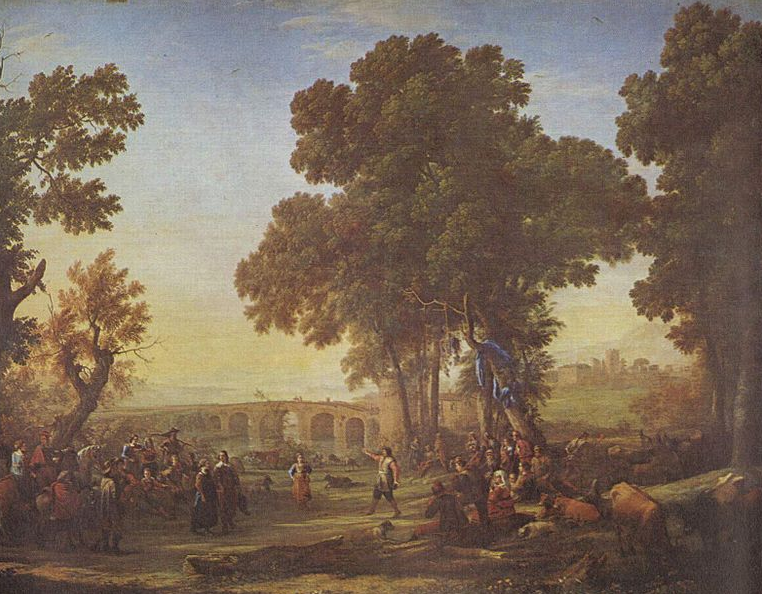






 ~ A Free Fiction Fix ~
~ A Free Fiction Fix ~ ~ Inspirational Regency Book Recommendations ~
~ Inspirational Regency Book Recommendations ~ ~ Guest Posts ~
~ Guest Posts ~


 Collette Cameron, a Pacific Northwest native, was born and raised in a small town along the northern Oregon coast, which to this day, continues to remain one of her favorite retreats. An enthusiast of times gone by, Collette currently writes Regency historical romance.
Collette Cameron, a Pacific Northwest native, was born and raised in a small town along the northern Oregon coast, which to this day, continues to remain one of her favorite retreats. An enthusiast of times gone by, Collette currently writes Regency historical romance.