Vanessa here,
“It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.”

So begins the words to the novel, Pride and Prejudice, and with it the love affair we have for 1800’s England. Now many of us may have been introduced to Jane Austen because of a high school literature assignment or catching a BBC or a Hollywood version of one of her books. I have come to know and appreciate her talents for unlike me, she was a contemporary author writing of her times, of the societal norms and taboos. Austen excelled at capturing the mood of the classes and the roles of women. Her words allow us to visit that time and space we lovingly call the Regency.
So today, I’d like to spend a few moments highlighting the amazing woman, Jane Austen.
Her Birth
Born December 16th, 1775, Jane Austen was the second daughter, the seventh child of eight for Reverend George Austen and Cassandra Austen. They lived in Steventon, Hampshire. They weren’t a rich family at £ 600 per annum. So Jane would find herself very much like her character, Elizabeth Bennett, with nothing more than her charms to recommend her.

Her Education
She learned as most girls did at home, to draw, play the piano, and the running of a household. From 1785 to 1786, she and her sister, Cassandra were sent to an aunt in Oxford for more studies. They were later sent to the Abby Boarding School in Reading.
Her Love of a Good Book
By 1801, Jane’s father possessed a large book collection of over 500 books. She is described by family members as a great reader. Her favorites included Fanny Burney’s Cecilia and Camillia and Samuel Richardon’s Sir Charles Grandison, and Maria Edeworth’s Belinda.
In Jane’s Northanger Abby, she puts up a defense of the reading and novels:
“There seems almost a general wish of decrying the capacity and undervaluing the labour of the novelist, and of slighting the performances which have only genius, wit, and taste to recommend them… In short, only some work in which the greatest powers of the mind are displayed, in which the most thorough knowledge of human nature, the happiest delineation of its varieties, the liveliest effusions of wit and humour, are conveyed to the world in the best-chosen language.”
Her Love Life
From her letters, one can see a few men came a courtin’ but she found most wanting: Heartley, Powlett, Lefroy.
In one of her correspondences, she writes:
“Tell Mary that I make over Mr. Heartley and all his estate to her for her sole use and benefit in future, and not only him, but all my other admirers into the bargain wherever she can find them, even the kiss which C. Powlett wanted to give me, as I mean to confine myself in future to Mr. Tom Lefroy, for whom I do not care sixpence. Assure her also, as a last and indisputable proof of Warren’s indifference to me, that he actually drew that gentleman’s picture for me, and delivered it to me without a sigh.”
Then later we find this:
“At length the day is come on which I am to flirt my last with Tom Lefroy, and when you receive this it will be over. My tears flow at the melancholy idea.”
And with the end of things with Mr. Lefroy, Jane’s friend (Mrs. Anne Lefroy, cousin to Tom Lefroy) even tried to play match maker. Mrs. Lefroy tried to fix Jane Austen up with the Rev. Samuel Blackall, a Fellow of Emmanuel College. It didn’t work out (See our take on Blackall). Perhaps her joy of writing claimed all her love. Or was she too poor to make a man fall violently in love with her.
Her Writing
Jane started her writing “career” with short stories. These pieces varied from witty to satirical. Many of these short stories were collected together and called the Juvenilia. Over 20 different shorts fill this collection with the most famous being: The Beautiful Cassandra, Love and Friendship, and The History of England.
Her published works (the ones published during her lifetime or posthumously by family members are included below: (S=Synopsis, W=Link to the Whole Work. Go ahead and download a copy provided for free.)
- Sense and Sensibility (1811) S W
- Pride and Prejudice (1813) S W
- Mansfield Park (1814) S W
- Emma (1815) S W
- Northanger Abbey (1817) S W
- Persuasion by Jane Austen (1817) S W

Her Death
Jane Austen died in 1817 at the age of 41. She began to get ill in 1816 and the yearlong decline, tapped her energy and made her in the end bed-ridden. The cause of her death is disputed. Some venture it was lymphoma. Others Addison’s disease. Another view is she died from bovine tuberculosis contracted by drinking unpasteurized milk. As I check the label, on the milk cartoon for my coffee, I’ll add a final potential cause, typhus, a recurrent form of the disease developed from a childhood illness. Her death left two more manuscripts unfinished, Sanditon (1817) and The Watsons (1804). She is buried at Winchester Cathedral in Winchester, Hampshire.

Well, I think we should all agree, her life was too short. Nonetheless, judging by the longevity of her work, she may just have accomplished what she was born to do. Share with us a favorite Jane Austen line or scene and why it sticks with you.
References:
- Images are from Wikipedia/Wiki commons.
- Wikipedia
- Project Gutenberg
- Pemberly.com
This week we’re giving away a lovely set of Jane Austen note cards.

For a chance to win, please leave a comment on any of the posts this week. winner will be drawn Monday, August 12. Winner must have a mailing address within the United States.
Originally posted 2013-08-05 10:00:00.
 Two centuries ago, a book was published that would impact the world of romantic literature forever. This year marks the two hundredth anniversary of Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice.
Two centuries ago, a book was published that would impact the world of romantic literature forever. This year marks the two hundredth anniversary of Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice.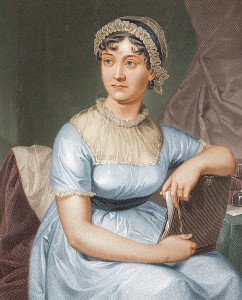
 A Gentlewoman’s Guide to Opium Addiction: How to Tell if Your Mr. Right Has Been Tokin’, Smokin’ or Shootin’ the Poppy ~ Guest Post by Michelle Griep
A Gentlewoman’s Guide to Opium Addiction: How to Tell if Your Mr. Right Has Been Tokin’, Smokin’ or Shootin’ the Poppy ~ Guest Post by Michelle Griep Miri Brayden teeters on a razor’s edge between placating and enraging her brother, whom she depends upon for support. Yet if his anger is unleashed, so is his madness. Miri must keep his descent into lunacy a secret, or he’ll be committed to an asylum—and she’ll be sent to the poorhouse.
Miri Brayden teeters on a razor’s edge between placating and enraging her brother, whom she depends upon for support. Yet if his anger is unleashed, so is his madness. Miri must keep his descent into lunacy a secret, or he’ll be committed to an asylum—and she’ll be sent to the poorhouse. 









 I rented a condo for a week with all my brothers and their families on an island off Savannah. It was a blast. Bike riding, cooking fresh seafood, watching movies until late. No takers on P&P though.
I rented a condo for a week with all my brothers and their families on an island off Savannah. It was a blast. Bike riding, cooking fresh seafood, watching movies until late. No takers on P&P though.




